Blog
Keep up to date with the latest news from art markets across the world through our blog "the eye of the expert"
Any questions?
contact@mr-expert.com
How to calculate the price of a diamond?
King of precious stones, a miracle of nature, the unique characteristics of the diamond make it the most expensive and sought-after stone on the gem market. If you would like to purchase a diamond, the question of its price is of course the most important one. But what are the criteria that influence their prix?
It is important to keep in mind that there is no such thing as a diamond course for the simple reason that every gemstone is different, so there are many factors that make your diamond unique.
The “4 C” of diamond valuation criteria
Since 1939, the “4 C” system has become THE reference for describing the specific characteristics of diamonds. The price of a diamond on the market depends on the combination of four criteria: Cut, Colour, Clarity and Carat. It is therefore important to take a holistic approach and not to focus on any one criterion in isolation.
- – Carat: It should be recalled in the preamble that the metric carat is the universal unit of measurement for the weight of a diamond, one carat corresponding precisely to 0.2 grams. Unlike other products, it is not enough to multiply the price per carat by the weight of the diamond to know its value. The larger the diamond, the rarer it is and the higher its price per carat, for the same quality. Therefore, we will always speak of the price per carat and not the price of the whole diamond.
- – Colour: A brilliant white colour is expected, a total absence of colour which then results from the sum of all the colours in the prism. The shades of white of white diamonds vary from colourless called D (Pure White) to yellowish hues resulting from the presence of gas atoms present during the crystallisation stage.
- – Clarity: Clarity is defined as the absence of inclusions, these natural signatures of the stone visible and measurable under x10 magnification are considered defects. Nevertheless, as no crystal is absolutely pure, there is always an infinitesimal proportion of foreign elements.
- – Cut: variable parameter, this is the only one of the “4 C” where the intervention of the human hand is noted, the rough natural diamond will then be sublimated by becoming a cut, sculpted or polished diamond. It is thus the meticulous cutting of the diamond into perfectly symmetrical facets that will allow the refraction of light and diffuse its brilliance.
The Rapaport Diamond Report: a reference matrix
As mentioned above, there is no diamond price as such, but there are price lists that serve as a reference for diamond dealers and traders around the world to calculate the unit price of a cut diamond: the Rapaport Diamond Report. These were invented in 1978 by Martin Rapaport, son of a diamond dealer who graduated from the GIA (Gemological Institute of America). Strongly criticized at its creation, this report will put an end to the manipulation and opacity of diamond prices.
The Rapaport Diamond Report consists of various price tables accessible only by subscription for professionals and are updated regularly: prices that have increased are marked in bold, while those that have decreased are marked in italics.
The price lists are based on:
- – of the weight (from 0.01 to 5.99 carats);
- – the shape of the diamond cut: a list exists for round diamonds and another one for special shapes (asscher, cushion, pear, princess, etc);
- – the colour and purity of the stone.

Each grid is composed of boxes, in each of which is a number representing the price of the diamond per carat in hundreds of US dollars.
Let’s decipher this table together:
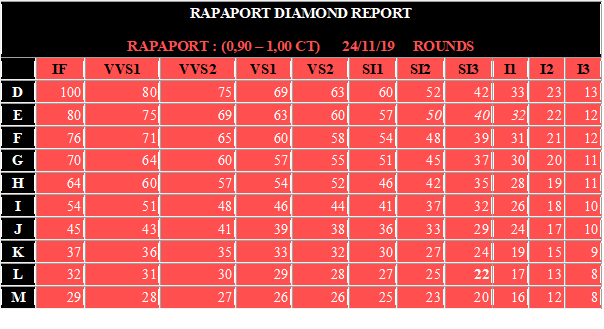
Firstly, on the first line of the table is the weight of the diamond in carat, the date of the report and the shape of the cut.
Then, on the second line of the table is the diamond purity scale from IF (Internally Pure) to I3 (Inclusions, we will speak of diamond “piqué” in common parlance).
Then, in the first column is the diamond colour scale from D (Pure White) to M (Tinted).
Finally, to find out the diamond price in dollars per carat, simply move horizontally and vertically by colour and clarity and add two 0’s to the number in the box.
Have you been able to follow? Now it’s your turn: what is the price of a 1.00 carat round diamond in L colour and clarity SI3?
Answer: The price of a diamond with these characteristics is 22 in our table. Its exact price would therefore be 1.00 carat x 22 x 100 = 2 200 $.
Recognised certification: an additional guarantee
Finally, it should be noted that a certified diamond will be easier to value and sell. This paper guarantor is very useful to know the quality of a diamond without being a professional.
Certificates of authenticity and quality protect you from deception and arbitrariness. The most recognised in the profession are issued by one of the following laboratories: GIA (Gemological Institute of America), IGI (International Gemological Institute) and HRD (Hoge Raad voor Diamant).
Our experts are at your disposal to inform you about the price of a diamond or a piece of jewellery and to carry out a possible sale.
You may also like
Find out how much your items are worth with Mr-Expert.com